Improving Reading Comprehension with Abstract Words using Augmentation, Linguistic Features and Voting
Abstract
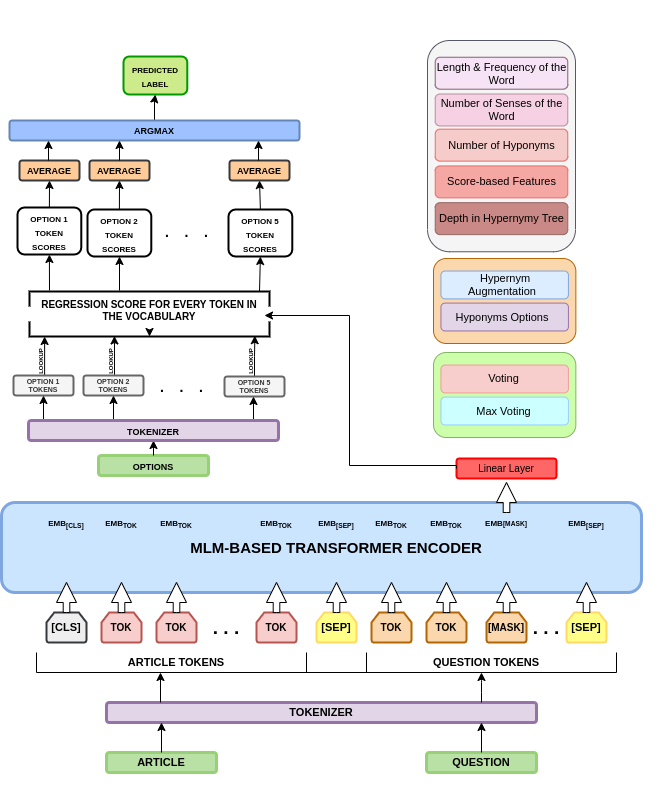
We present our approaches and methods for SemEval-2021 Task-4 Reading Comprehension of Abstract Meaning. Given a question with a fill-in-the-blank, and a corresponding context, the task is to predict the most suitable word from a list of 5 options. There are three subtasks: Imperceptibility, Non-Specificity and Intersection. We use encoders of transformers-based models pretrained on the MLM task to build our Fill-in-the-blank (FitB) models. Moreover, to model imperceptibility, we define certain linguistic features, and to model non-specificity, we leverage information from hypernyms and hyponyms provided by a lexical database. Specifically, for non-specificity, we try out augmentation techniques, and other statistical techniques. We also propose variants, namely Chunk Voting and Max Context, to take care of input length restrictions for BERT, etc. Additionally, we perform a thorough ablation study, and use Integrated Gradients to explain our predictions on a few samples. Our models achieve accuracies of 75.31% and 77.84%, on the test sets for subtask-I and subtask-II, respectively. For subtask-III, we achieve accuracies of 65.64% and 64.27%.